
Smooth Data Collection Process | 6 Tips for Research
When your experiment is ready to go, here are a few straightforward tips to consider in your data collection procedure just before you fully launch your experiment. Some of these are especially useful if you are running a remote / online study!
1. If crowdsourcing, start with a few subjects first
If you are using crowdsourcing to recruit participants for your experiment, we recommend piloting with just a few subjects at first!
- ie. just collect 5 subjects and if everything goes well and according to your expected data collection plan, then increase the participant count to 50 or 100, etc.
- It's just a much safer option and is actually considered best practice!
2. Consider mobile-specific nuances
If you are allowing mobile/phone-based participation (which is a default on some crowdsourcing platforms like Prolific), be aware of some mobile-specific nuances.
- For example, automatic audio playing does not work on iPhones at all (in the browser)! This is true for Safari on iOS and even for Chrome on iOS because Chrome on iPhones is not Chrome but just Safari with a different skin (totally weird, but true).
- In general, browsers on iPhones do not allow audio to be played without a so-called ‘user gesture’ (like a button press). This is just basic Apple Policy and has nothing to do with online experiments or Labvanced at all.
- So, this is an important thing to keep in mind and you can ensure that your experiment setup addresses these mobile-specific nuances so that there are not any surprises during the data collection process.
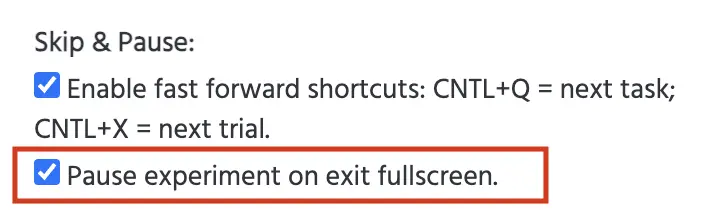
3. Pause experiment if the participant exits full screen mode
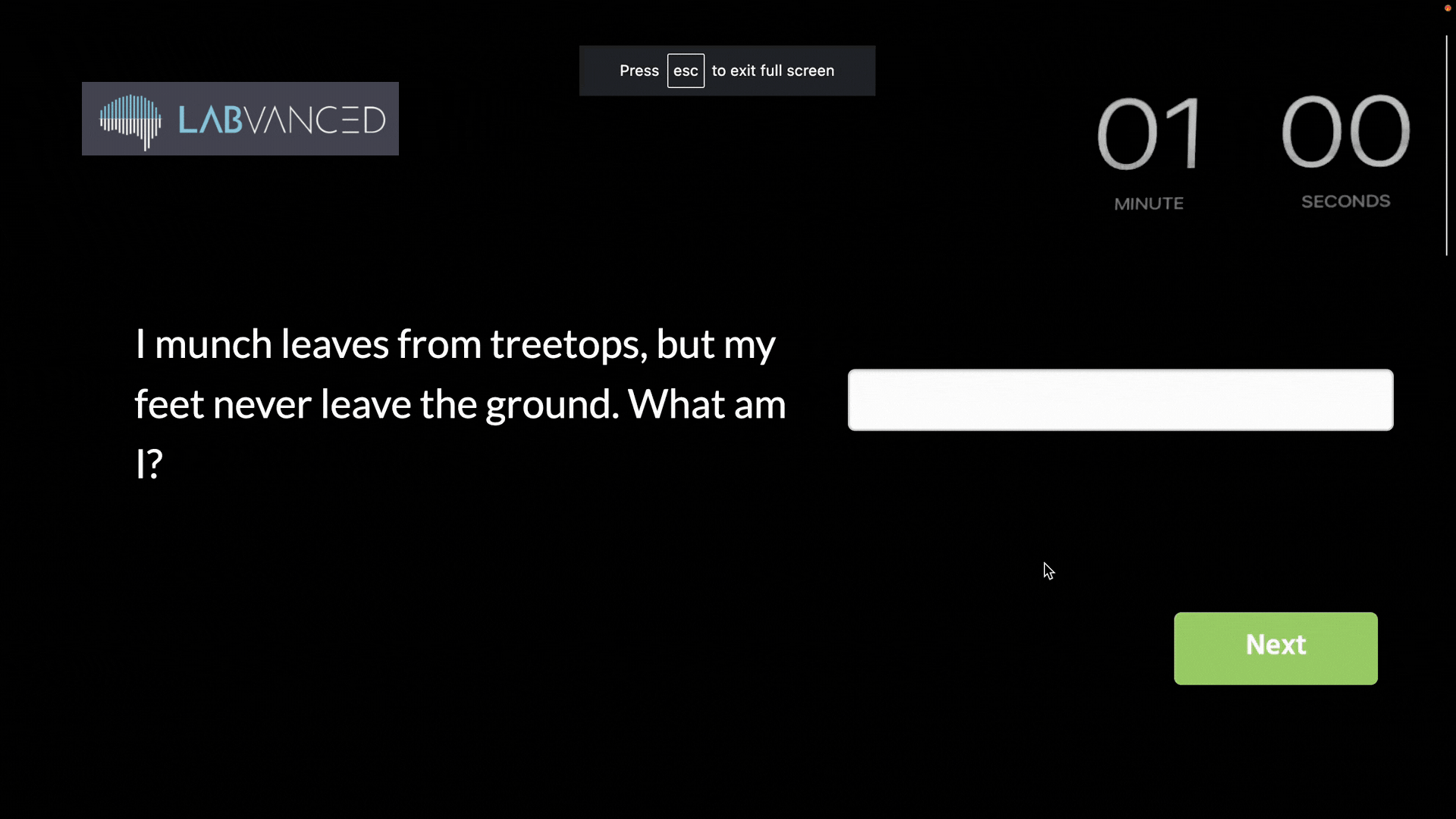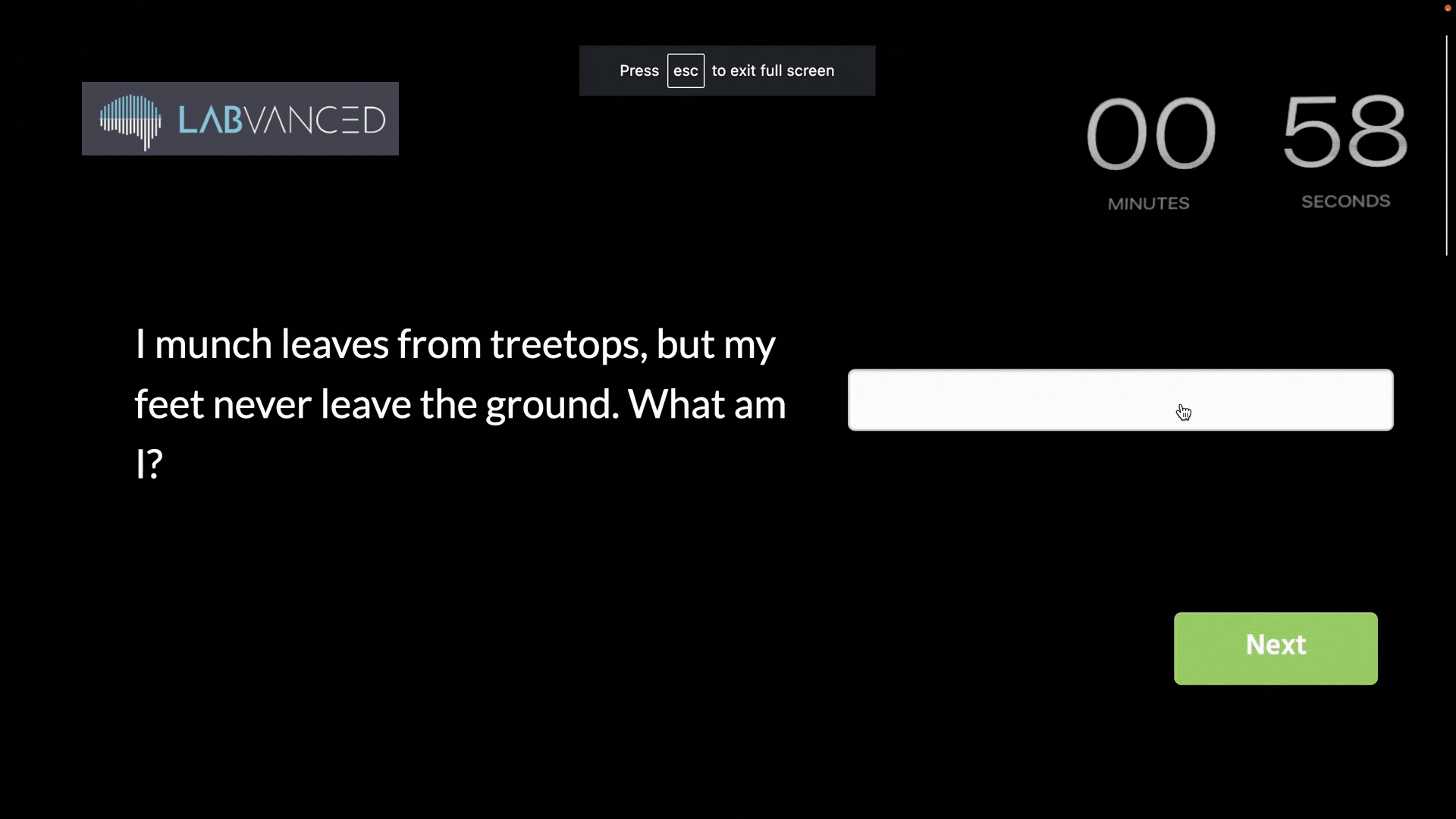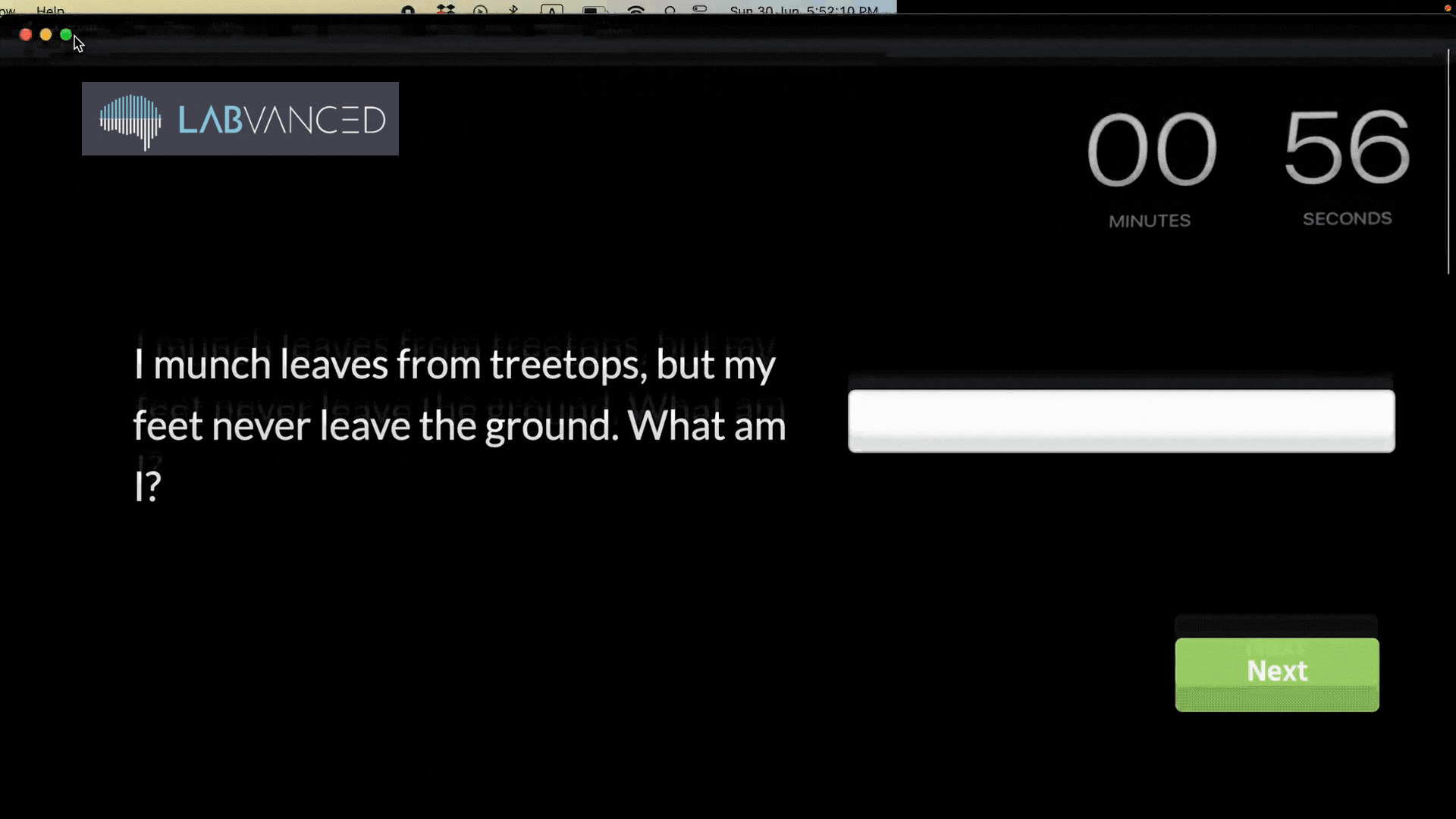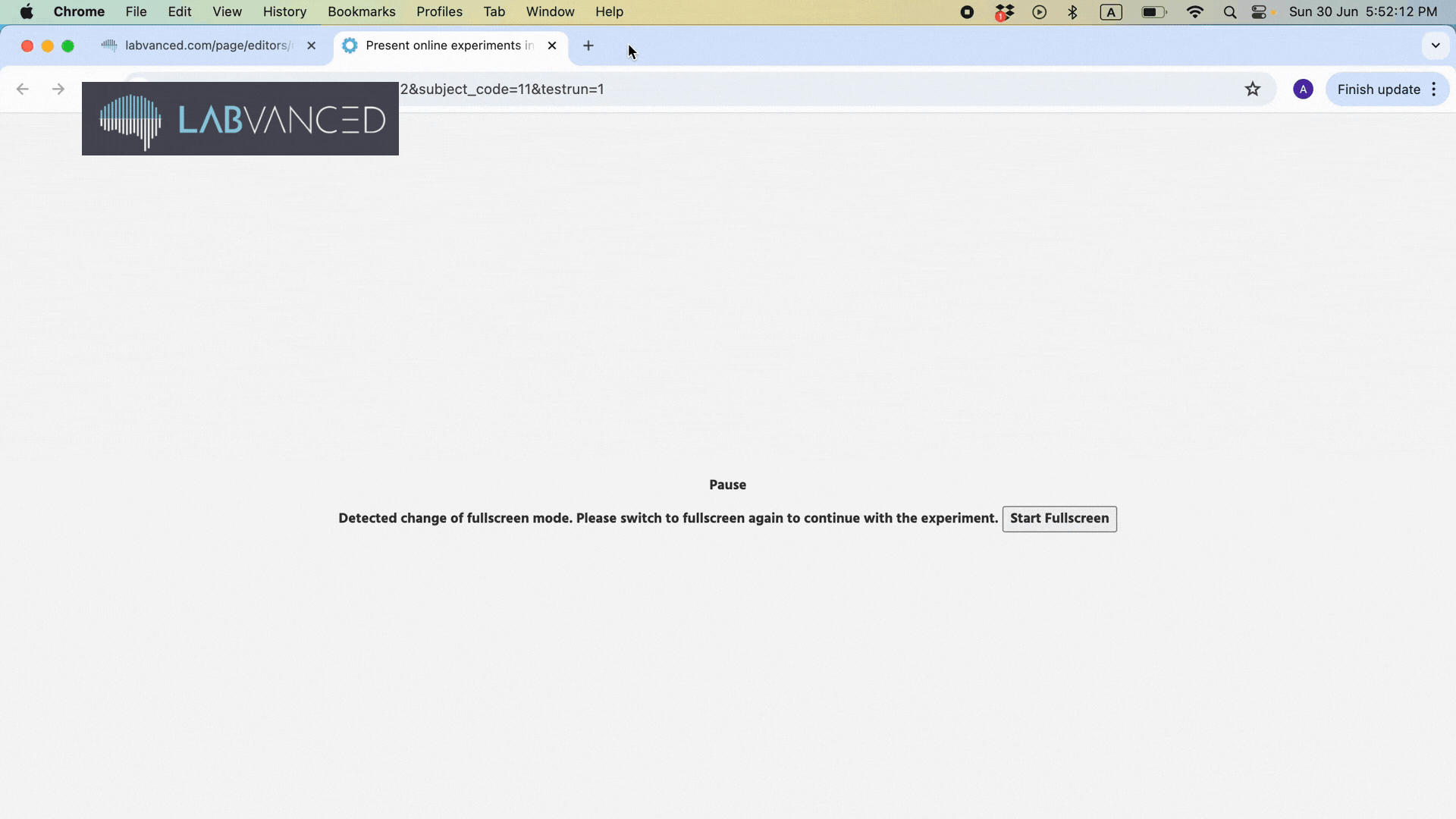
Remote / online studies are meant to be in full screen mode so that the participant is 100% focused during the experiment. If a subject leaves fullscreen mode or switches to another tab, your study integrity can get compromised and even recordings can get lost (which is not such ideal for any data collection procedure or plan).
In Labvanced, under the ‘Study settings’ tab in the ’Startup & Main Settings’ column, there is an option to ‘Pause experiment on exit fullscreen.’ This option should be enabled! This way, if the participant leaves the full screen mode, the experiment will automatically be paused.
Below, you can see an example of an experiment that was immediately paused as soon as the participant exited the fullscreen mode:
4. Add variables to collect data with regards to system specifications and full screen status
Can you know if the participant, at any point during the study, exited the fullscreen mode? Yes!
There are system variables automatically available to all studies created with Labvanced that can be used for this purpose and you can use them to record this behavior, so consider adding them to your data collection plan! Here are a few examples you can use for data collection:
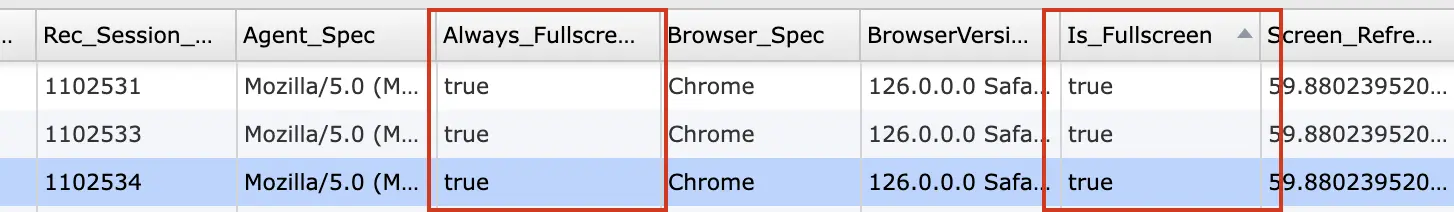
- Always_Fullscreen: Essentially, a boolean value is reported as ‘true’ as long as the participant keeps the experiment running in fullscreen mode. This can be used to pause and even quit the experiment when a participant leaves fullscreen mode.
- Is_Fullscreen: Another boolean variable where a true/false value is reported if the experiment is currently being viewed in fullscreen mode. The value can change throughout the course of the experiment and can be measured across time as a part of your data collection process.
The image below is a data collection example of these variables in action:
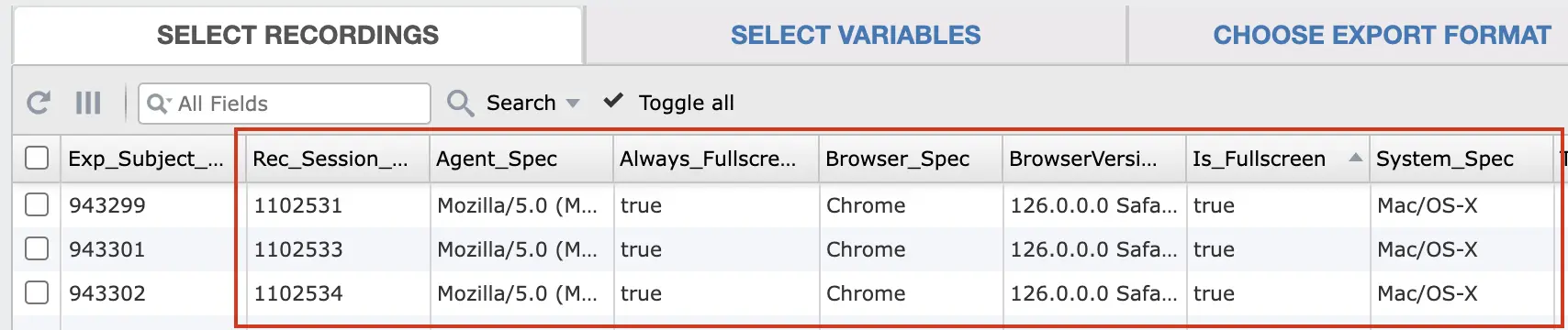
You can also incorporate the some of the following system variables in your data collection procedure to record factors like browser specifications and system specifications:
- Browser_Spec: Browser_Spec holds the value of the browser used by the participant to perform the experiment. This can be used to later analyze possible differences between browsers.
- BrowserVersion_Spec: BrowserVersion_Spec holds the value of the browser version used by the participant to perform the experiment. This can be used to later analyze possible differences between browser versions.
- System_Spec: System_Spec holds the value of the operating system/device used by the participant to perform the experiment. This can be used to later analyze possible differences between operating systems/devices.
If you are conducting remote / online studies, considering different browsers or system specifications, as well as full screen status, may be relevant for your data collection plan, so it’s worth a note to include them before launching your study.
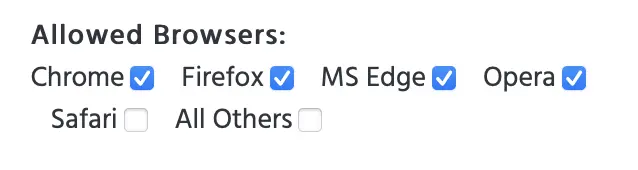
5. Consider disabling Safari as an allowed browser
This is an important point when working with online / remote studies… Why? Safari is notorious for having outdated APIs and working differently. Thus, this is bound to impact the integrity of the data collection procedure you had planned.
- As a browser, we don’t recommend Safari for online studies especially for advanced studies (such as those that employ webcam-based eye tracking).
- Mac users usually have other options available, so disabling Safari should be okay.
- In Labvanced, this browser is automatically disabled for this reason. You can double check this under the ‘Study settings’ tab and in the ’Browsers & Devices’ column, making sure that ‘Safari’ as an option is not selected.
6. Disable shortcuts
- Commonly used keyboard shortcuts can be used unless you disable them. For example, a participant may be able to press ‘ctrl+x’ to skip trials.
- To disable this, simply go to your ‘Study Settings’ tab and under the ‘Startup & Main Settings’ column, disable this option.
Conclusion
Overall, these tips are relatively simple and easy to implement in your data collection procedure and in the long run they can significantly boost the quality of the data that you collected in your research!
